CLS
Cumulative Layout Shift
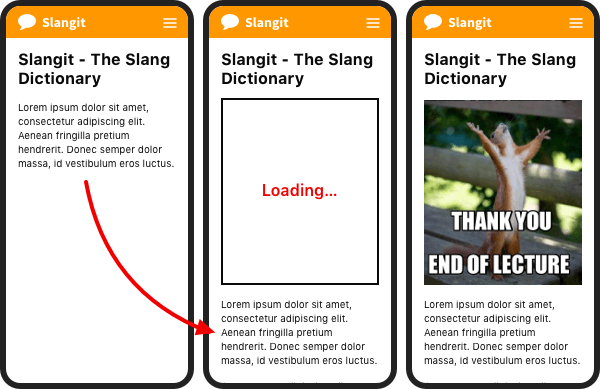
Example
Our web developer carefully structured the elements on this page to reduce our CLS score and improve user experience
Related Slang
| Core Web Vitals | Metrics that measure the user experience of a website |
| LCP | Largest Contentful Paint |
| FID | First Input Delay |
| SEO | Search engine optimization |
| EAT | Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness |
| SERP | Search engine results page |
| UX | User Experience |
| UI | User Interface |
 Can you score under par in this golf terms quiz?
Can you score under par in this golf terms quiz?
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) is a metric used by web developers to measure the visual stability of a webpage. Google introduced CLS in 2020 as one of the core web vitals for objectively analyzing a website’s user experience (UX).
As soon as a webpage loads, the user begins to consume the page’s content by reading text, studying images, and interacting with buttons. If the content on the page unexpectedly shifts, the user could become annoyed or confused. In the worst cases, content shifts can cause a user to click a button or link that he or she didn’t intend to click. CLS attempts to measure this kind of negative user experience.
A layout shift is when the start position of an element in the viewport changes. Adding a new element to the page is not considered a layout shift unless the new element causes other elements within the viewport to change position. Using the CSS transform property to modify an element’s position is also not considered a layout shift since this transformation does not affect surrounding content.
Not all layout shifts have a negative impact on user experience. For example, a user may click a button to load more content and reposition existing elements. To account for expected shifts, Google excludes layout changes that occur within 500 milliseconds of user interaction from the CLS measurement.
Google provides helpful tools to measure and improve CLS. Developers are encouraged to reduce the CLS score of webpages to 0.1 or less. To do this, developers should structure webpages that don't cause elements to be repositioned without user interaction. Developers should specify the dimensions of images and videos that could potentially shift content after being loaded.